The magic behind ConvNets
Friday, April 13, 20181 mins read
Ordinary neural networks consists of neurons that have learnable weights and biases. The input is a single vector (of features) that is transfomed through a number of hidden layers. Each hidden layer is made up of a set of neurons, where each neuron is fully connected to all neurons in the previous layer. In case of Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), the inputs are images i.e. the input has a third dimension, depth in additon to width and height.
ConvNets consists of layers. Every layer in ConvNet transform the 3D input volume (image). There are three types of layers used:
- Convolutional layer (Filtering): For a computer, it’s difficult to identify correct image as it literally matches them to decide if two imgages are similar. What ConvNets does is to compare images piece by piece; each piece being a feature. To calculate the match of a feature to a patch of image, it calculates the dot product between them. This dot product (b/w feature and image patch) is repeated for every possible image patch. The convolution layer performs this whole convolution process.
- Pooling layer reduces the spatial size, amount of parameters and computation in the network and hence, control the overfitting i.e. it takes large images and shrink them down without losing much information from them. Mostly, max-pooling is used in practice.
- FC (fully connected) layer computes the class scores (votes) for each image. In it, each neuron is connected to all the neurons in the previous layer.
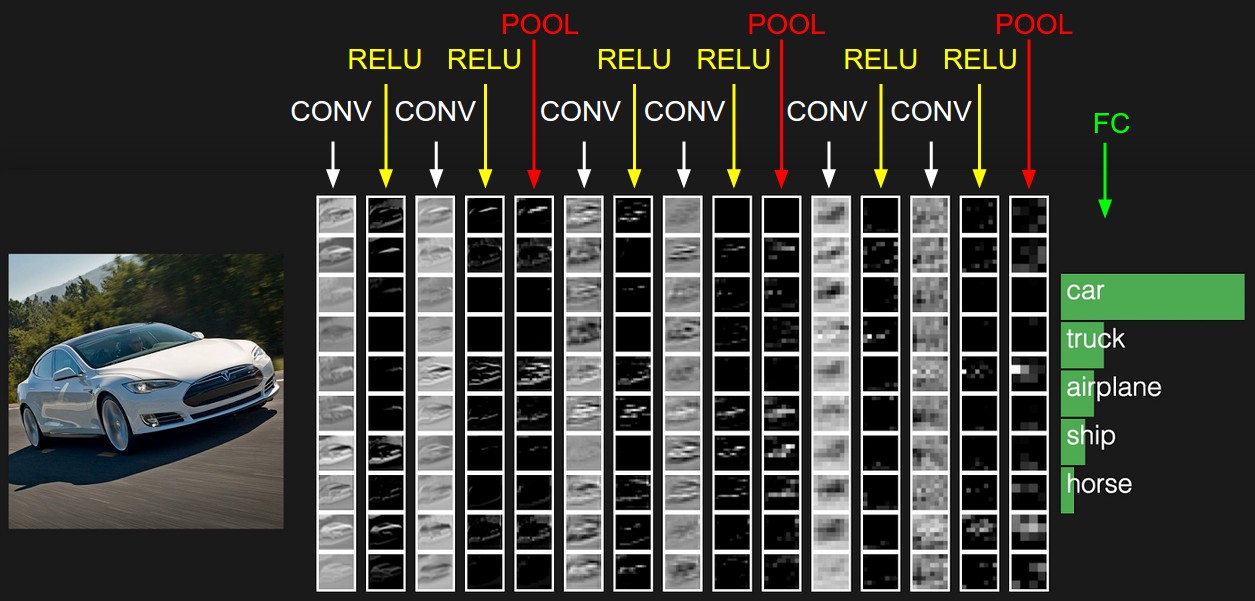
The amount of error in voting (right prediction - wrong prediction) tells us how good the features and weights are. Backpropagation is used for assigning the optimum weights to neurons.
Normalization layer: Sometimes, normalization layer is also used in ConvNets. Usually, it is Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU). ReLU, max(0, x), replaces the negative values in matrix with 0. RELU is just a non linearity which is applied as in neural networks.
References: